Advanced behavior correction for dogs with fear-based aggression
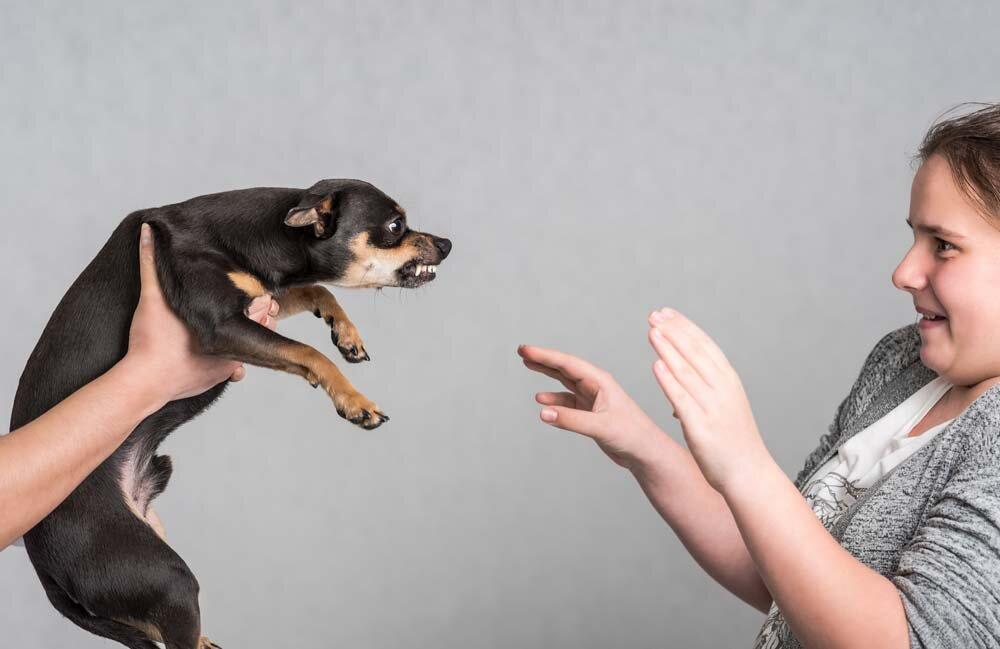

Fear-based aggression in dogs is a complex issue that challenges even the most experienced pet owners and trainers. Understanding and addressing this behavior requires a nuanced approach that goes beyond basic obedience training. This article delves into advanced behavior correction techniques specifically designed for dogs exhibiting fear-based aggression. By exploring the underlying causes of this behavior and offering step-by-step guidance, we aim to equip dog owners and trainers with the knowledge and tools necessary to foster a safe and harmonious environment. Whether you are dealing with a newly adopted rescue or a long-time family pet, these strategies will help you navigate the intricate dynamics of fear and aggression, ultimately leading to a more balanced and confident canine companion.
Understanding Fear-Based Aggression in Dogs
Fear-based aggression in dogs is a complex behavioral issue that stems from a dog’s instinctual response to perceived threats. Unlike other forms of aggression, which may be driven by dominance or territorial instincts, this type of aggression is primarily rooted in fear. Dogs exhibiting these behaviors often do so because they feel cornered or insecure, and their natural response is to protect themselves. Understanding the underlying triggers is crucial to addressing and correcting these behaviors effectively.
- Identify Triggers: Begin by observing situations that cause your dog to react aggressively. Common triggers include loud noises, unfamiliar people or animals, and specific environments.
- Gradual Desensitization: Introduce your dog to these triggers slowly and in a controlled manner. This process involves exposing your dog to the trigger at a low intensity and rewarding calm behavior.
- Positive Reinforcement: Reward your dog for displaying non-aggressive behavior in the presence of triggers. Use treats, praise, or toys to reinforce positive behavior.
- Consult a Professional: If the aggression is severe or persistent, consider working with a certified dog behaviorist who specializes in fear-based aggression. They can provide personalized strategies and support.
Implementing these techniques with patience and consistency can significantly help in reducing fear-based aggression in dogs, leading to a more harmonious relationship between you and your pet.
Identifying Triggers and Warning Signs
When addressing fear-based aggression in dogs, understanding the nuances of their behavior is crucial. The first step is to keenly observe your dog’s body language and environmental interactions. Look for subtle cues such as tensed muscles, pinned-back ears, or whale eye (showing the whites of their eyes) which can signal discomfort. Recognizing these early signs can help in preempting aggressive responses before they escalate. It’s essential to maintain a consistent environment to identify patterns in behavior effectively.
- Environmental Changes: Note if aggression occurs in specific locations or situations, such as during walks or when encountering other dogs.
- Social Interactions: Pay attention to how your dog reacts to new people or animals, and observe any consistent triggers.
- Sound Sensitivity: Loud noises or sudden sounds can be stressors; watch for signs of anxiety or fear when exposed to these.
- Resource Guarding: Monitor for aggression around food, toys, or resting spots, which can indicate territorial behavior.
By identifying these triggers and warning signs, you can better tailor behavior correction strategies that address the root cause of your dog’s fear-based aggression. A proactive approach will help in creating a safe and supportive environment for your pet.
Implementing Positive Reinforcement Techniques
Incorporating positive reinforcement techniques is a transformative approach for addressing fear-based aggression in dogs. This method centers on rewarding desired behaviors, which helps to gradually replace fear responses with confidence and calmness. Consistency is key; rewards should be given immediately after the desired behavior to strengthen the association. Start by identifying triggers that cause fear-based aggression in your dog. Once identified, create a controlled environment where these triggers can be introduced at a low intensity. This allows your dog to experience the trigger without reaching a threshold of fear.
- Use high-value treats that your dog loves, ensuring they are motivated to earn them.
- Employ clicker training to mark the exact moment your dog exhibits a calm behavior in the presence of a trigger.
- Gradually increase the intensity or proximity of the trigger, maintaining a focus on your dog’s comfort level.
- Include verbal praise along with treats to reinforce positive actions.
By systematically rewarding calm behavior, your dog will begin to associate previously fear-inducing situations with positive outcomes, reducing aggression over time. This strategy not only addresses the immediate issue but also fosters a stronger bond between you and your pet, built on trust and mutual respect.

Creating a Safe and Supportive Environment
When addressing fear-based aggression in dogs, it is crucial to cultivate an environment where your pet feels both secure and supported. This begins with creating a space that minimizes stress and encourages positive behavior. Ensure your dog has access to a designated area that is quiet and free from potential triggers. This might include using baby gates to restrict access to certain areas or providing a comfortable crate as a safe retreat.
- Consistent Routine: Establish a daily routine for feeding, walks, and playtime. Predictability can significantly reduce anxiety in dogs.
- Positive Reinforcement: Reward your dog for calm behavior with treats, affection, or play. This helps them associate positive experiences with their environment.
- Safe Interactions: Gradually introduce your dog to new people and pets in controlled settings. Use a leash and keep a safe distance until your dog shows signs of comfort.
Implementing these strategies with patience and consistency can significantly impact your dog’s ability to manage fear-based aggression. Remember, the goal is to foster trust and security, allowing your dog to thrive in a nurturing atmosphere.



