Is Positive Reinforcement the Only Humane Way to Correct Behavior
In recent years, the conversation surrounding behavior correction, whether in children, pets, or even ourselves, has increasingly turned towards positive reinforcement as the gold standard. With its focus on rewarding desired actions rather than punishing unwanted ones, positive reinforcement is often hailed as the most humane and effective method for encouraging good behavior. But is it the only compassionate option available? This article delves into the principles of positive reinforcement, examines its effectiveness, and explores whether other humane methods can also play a role in fostering positive behavioral change. Join us as we unravel the complexities of behavior correction, aiming to understand if positive reinforcement truly stands alone in its humane approach, or if there’s room for a broader perspective.
Understanding Positive Reinforcement and Its Benefits
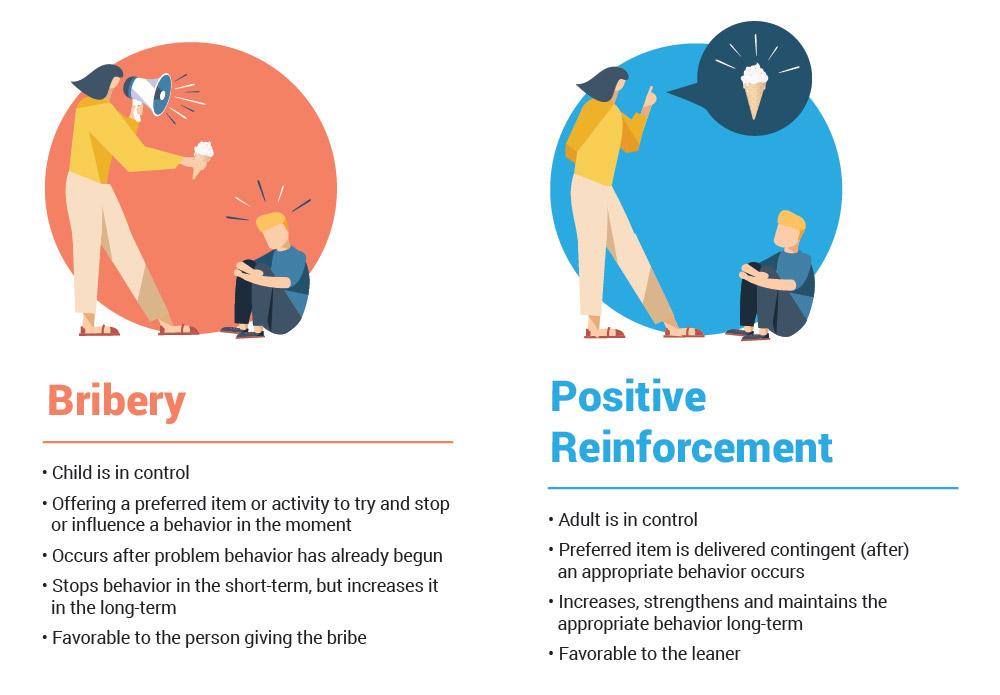
Positive reinforcement is a cornerstone in behavioral psychology, leveraging the power of rewarding desired actions to encourage their recurrence. This approach is not only effective but also nurtures a supportive and compassionate environment. By focusing on rewarding good behavior rather than punishing the bad, individuals—whether they be children, pets, or even adults—are more likely to feel motivated and valued. This method fosters a learning atmosphere that emphasizes growth and improvement, rather than fear of retribution.
Consider the myriad benefits that come with this approach:
- Increased Motivation: Receiving positive feedback encourages individuals to continue engaging in the desired behavior.
- Improved Self-Esteem: Recognizing achievements boosts confidence and promotes a positive self-image.
- Stronger Relationships: A reinforcement-based approach builds trust and strengthens bonds between the individual and the reinforcer.
- Long-term Behavioral Change: Positive reinforcement often leads to lasting change as behaviors are associated with positive outcomes.
Incorporating positive reinforcement into everyday interactions not only corrects behavior but also enriches the lives of those involved, creating a more harmonious and understanding world.

Exploring Alternative Humane Behavior Correction Methods
When considering behavior correction, many people immediately think of positive reinforcement as the go-to humane method. However, there are various other approaches that can be both effective and compassionate. Cognitive-behavioral techniques, for instance, focus on understanding the underlying causes of behavior and addressing them through mental and emotional awareness. This method encourages individuals to reflect on their actions and the thoughts that drive them, fostering a more profound internal change.
Another alternative is the use of environmental adjustments. This approach involves modifying the surroundings to naturally guide behavior in a desired direction. For example, creating an enriching environment that meets an individual’s needs can significantly reduce unwanted behaviors. Some effective strategies include:
- Providing engaging activities that cater to specific interests or skills.
- Ensuring clear and consistent communication to prevent misunderstandings.
- Establishing structured routines that promote predictability and security.
These methods underscore the idea that humane behavior correction can extend beyond positive reinforcement, offering a broader spectrum of compassionate options.

Balancing Positive Reinforcement with Other Techniques
While positive reinforcement is celebrated for its humane and effective approach in encouraging desirable behaviors, it is important to remember that it can be complemented by other strategies to create a balanced behavior correction plan. Positive reinforcement involves rewarding desired behaviors to increase their occurrence, which is undeniably powerful. However, in some situations, using a combination of methods can lead to more sustainable results.
Consider the integration of negative reinforcement, where an unpleasant stimulus is removed to encourage behavior, or extinction, which involves ignoring unwanted behaviors until they decrease. Additionally, clear communication and setting boundaries can play crucial roles in behavior management. Some key techniques to consider include:
- Consistency: Ensure that rules and expectations are clear and consistently applied.
- Modeling: Demonstrate desired behaviors for others to emulate.
- Timeouts: Provide a break from activities to help individuals reset and refocus.
By understanding the unique needs and circumstances of each individual, a tailored approach that combines positive reinforcement with other techniques can often yield the best outcomes, fostering a supportive and effective environment for behavior correction.

Practical Tips for Implementing Humane Behavior Correction Strategies
- Understand the Root Cause: Before implementing any correction strategy, it’s crucial to identify the underlying reasons for the behavior. Whether it’s stress, lack of understanding, or unmet needs, addressing these root causes can lead to more effective and humane solutions.
- Focus on Communication: Clear and consistent communication is key. Use cues and signals that the individual can easily understand. This ensures they know what is expected and can adjust their behavior accordingly.
- Offer Choices: Providing options empowers individuals and can reduce resistance. When they feel they have control over their actions, they’re more likely to respond positively to correction efforts.
- Use Time-Outs Wisely: If a behavior needs to be interrupted, use time-outs as a moment for reflection rather than punishment. Ensure the environment during a time-out is calm and not isolating, promoting a sense of safety and understanding.
- Reinforce Positive Alternatives: Once the desired behavior is exhibited, reinforce it immediately. This can be through verbal praise, physical affection, or other forms of positive reinforcement that are meaningful to the individual.
Remember, the goal is to guide and educate rather than control or dominate. Humane behavior correction strategies should always prioritize the well-being and dignity of the individual involved, creating a foundation of trust and mutual respect.
Wrapping Up
the exploration of positive reinforcement as a humane method for correcting behavior highlights its effectiveness and compassionate approach. While positive reinforcement is not the only method available, its emphasis on encouragement and reward aligns well with a humane perspective, fostering an environment of trust and mutual respect. By focusing on what individuals or animals do right, rather than punishing what they do wrong, positive reinforcement not only corrects behavior but also builds confidence and motivation. It is important, however, to remain open-minded and consider that a combination of strategies may sometimes be necessary, tailored to specific situations and individual needs. Ultimately, the goal is to cultivate positive outcomes in a way that respects the dignity and well-being of all involved. As we continue to learn and grow in our understanding of behavior correction, embracing a compassionate approach will always be a step in the right direction.